I, a universe of atoms, an atom in the
Universe
Richard P. Feynman
American theoretical physicist
(Founder & Director of Bramhandiniyog Astronomy Research Institute)
The motion, function, modification and all activities are happening in our body is similar to the cosmos activities. Here we are just correlating with them to give the new and another view to understanding the Universe. If we observe our internal body function and compare with the cosmos events then we can solve biggest mysteries of cosmos. It will be easier to understand. The difference in events is happens in body in too much smaller as compare with cosmos, try to correlate it for our better understanding.
Atoms or
molecules are building blocks of all the matters whether it is
in our body or in
cosmos.........!
Ø Cell
A cell is a
basic unit of life as we know it. It is the smallest unit capable of independent
reproduction. Is a basic building block of living things. The human body is
composed of trillions of cells. For providing (shape) structure to the body, we
take nutrient from food, convert those nutrients into energy and carry out
specialized functions. Cells also contain the body’s hereditary material and
can make copies of themselves.
Single
celled organism is unicellular organism. ex. Amoeba- he reproduces himself. They
behave and work like multicellular organism i.e. like human. The life is start
from single cell like Universe started from big-bang. i.e. Human life
and life of Universe have same starting condition. The basic component of cell
is plasma membrane, it separates cell one another and form the surrounding
medium is porous and allows movement of substance or material inward as well as
outward. The membranes contain proteins that act as channel and pumps to take
out molecules from the cell. In addition to cell membrane, there is an outer
thick layer in cell of plants is a cell wall.
The
jelly like substance found between the cell membrane and nucleus is cytoplasm.
It provides a safe environment for all intra-cellular components. The cytoplasm
made from water, proteins, carbohydrates and lipids. Nucleus is a membrane
enclosed organelle found in the cells that is also known as control center of
the cell. Nucleus is always separate from cytoplasm by nuclear membrane. The
small spherical body inside the nucleus is nucleolus.
Chromosomes
are thread like structure located inside the nucleus of animal and plant cells,
but they are not always present, they form around the time of cell division.
Chromosomes carry genes which hold the information to build and maintain an
organism’s cells and pass genetic traits to offspring. Genes form a few
stretches of DNA, which is a nucleic acid that contain genetic instructions
used in development and functioning of all known organism.
The
cell having a well-organized nucleus and nuclear membrane are known as
eukaryotic cell. And a prokaryotic cell has a plasma membrane. They are
surrounded by semi fluid substance i.e. Cytosol. On which there is coating
called capsule and it protect the cell from stick to another surfaces.
Flagellum is a
tail like projection to it.
Ø Cosmos
Events
Like cell, the
big-bang is basic event of universal life. It is also capable to produce its
family i.e. stars, galaxies, planets and all heavenly objects.
Figure 1.1: Eukaryotic cell and prokaryotic cell
Like
cell, in the beginning of big-bang all the particles got a mass in Higgs field.
Same work is done by the cell. After these events all objects get separated by
collision and other forces as well, like cell separation. All objects in the
cosmos are made by some layers and they are transparently separated by each
other like cells are separated by porous. And it is allow for inward and
outward movements. Also we can say that both cell and cosmic object have outer
thick layer.
Like
chromosomes in cell, they are appear only when cell division process same thing
happen in the star also. Some unknown parts of its core come into appearance
after its collision with others or at blast. i.e. Supernovae. In cell, a
chromosome carries information through genes and is helpful for development and
functioning of known organism. Same thing occur in star blast, we collecting the
information from its remnants and emitted rays in the range of gamma-rays,
x-ray and visual range.
The
same process occurs in the cell as well as in the star cycle. Yet we don’t know
exactly what is happening in the star cycle..? Hence we just need to understand
what is exactly going on in the cell, and then automatically we can solve all
unknown mysteries about star and its life cycle.
Figure 1.3: Cell nucleus and star nucleus
Ø Mitosis
and Meiosis
Mitosis and
Meiosis are both types of cell division. They both deal with
replication of
chromosomes. The chromosomes are divided in a similar
way and
transported to newly formed cells. Some of the stages resemble
each other in
significant way.
Ø Mitosis
If a cell wants
to make a duplicate of itself then, they must copy its DNA (part of a chromosome).
And they separated and sorted into two sides of the cell. The cell then split
in to two parts. Part of each parent is carried to the two new cells. Results
in cells such as internal organs, skin, bones, blood etc. There are few stages
of mitosis such as,
Ø Inter-phase
- Pro-phase (preparation phase) - Meta-phase (organizational phase) - Ana-phase
(Separation phase) - Telo-phase.
After
mitosis the actual splitting of the daughter cells into two separate cells is
known as cytokinesis. And occurs differently in both plant cells and animal
cells. Finally, the new identical cell separates and once again they enter into
inter-phase in preparation for a later mitotic division. While the chromosomes
are no longer visible, they will be replicated just before mitosis begins.
Figure 1.4: Stages of mitosis
Ø Meiosis
Meiosis I- Has
four phases as,
Ø Pro-phase
I - Meta-phase I - Ana-phase I - Telophase I
Meiosis II
The meiosis I is
really similar to mitosis. The only difference is that the two chromatids per
chromosomes are not necessarily identical due to genetic recombination
occurring in meiosis I.
Ø Pro-phase
II - Meta-phase II - Anaphase II - Telophase II
The four
daughter cells are now all haploid and have the right amount of DNA. They are
ready to develop into sperm or eggs now.
Figure 1.5: Stages of meiosis
Ø How
star is born...?
Imagine an
enormous cloud of gas and dust, many light-years across. Gravity, as it always
does, tries to pull the materials together. A few grains of dust collect a few
more, then a few more, then more still. Eventually, enough gas and dust has
been collected into a giant ball, at the center of the ball, the temperature
from all the gas and dust bumping into each other under the great pressure of
the surrounding material reaches 15 million degrees or so. A wondrous event
occurs....nuclear fusion begins and the ball of gas and dust starts to glow. A
new star has begun its life in our Universe.
!!Like
cell starts its life in our body..!!
So, what is this
material, called “nuclear fusion”......? And why
does it start
happening inside the ball of gas and dust..? It happens like
this...As the
contraction of the gas and dust progresses and temperature
reaches 15
million degrees or so, the pressure at the center of the ball
become enormous.
The electrons are stripped off of their parent atoms,
creating a
plasma. The contraction continues and the nuclei in the plasma start moving
faster and faster. Eventually, they approach each other so fast, that they
overcome the electrical repulsion that exists between their protons. The nuclei
crash into each other so hard that they stick together, or fuse. In doing so,
they give off a great deal of energy. This energy from fusion pours out from
the core, setting up an outward pressure in the gas around it the ball of gas and
dust, it moves off into space in the form of electromagnetic radiation. The
ball, now a star, begins to shine.
New stars come
in a verity of sizes and colors. They range from blue
to red, from
less than half the size of our Sun to over 20 times or more the Sun size. It
all depends on how much gas and dust is collected during the stars formation.
The color of the star depends on the surface temperature of the star. And its
temperature depends, again on how much gas and dust were accumulated during
formation. The more mass a star starts out with, the brighter and hotter it
will be. For a star, everything depends on its mass.
Throughout their
life, stars fight the inward pull of the force of gravity. It is only the
outward pressure created by the nuclear reactions pushing
away from the
star core that keeps the star “intact”. But these nuclear
reactions
require fuel, in particular hydrogen. Eventually the supply of
hydrogen runs
out and the star begins its demise.
Just observe the
cell evolution in our body universe and star evolution
in the
cosmos......!! Answers of all mysterious questions will solve
Ø Co-relation
between Cell and Star
Each minute our
body needs to make about..300 million new cells..! A cell spends a good part of
its life in inter-phase as working and growing, breaking the sugars,
synthesizing proteins, enzymes. However, cells inevitably wear out, break down
and suffer injuries.
Just think, the
star is born with millions of atoms (photons) collecting
together, then
its mass is depends on the how much gas is trapped during
formation. The
fusion reaction is going on that time, the star is at good
condition.
Similarly like the cell is at inter-phase stage. After that, time
goes on then
fuel is burn out and star will dead with supernovae or hypernovae and form
white dwarf, neutron star or black hole. Same thing is happening in the cell
cycle also. Its constituent particles (atoms) may be different but its process
is same.
!!That means
Cells are the stars of our body Universe..!! Still yet we
don’t know
confidently how the planets were formed.
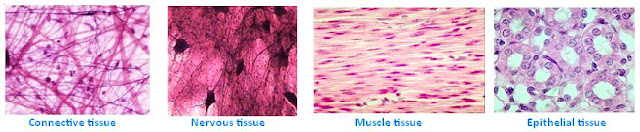
Ø Tissue
Is a group of
cells that perform a similar function. These are in unicellular organisms. Four
categories of tissue in the human body,
i) Epithelial
tissue:-Covers
body and organ surface, line body cavities and forms glands. Is involved with protection,
absorption, excretion, secretion, diffusion and filtration.
ii) Connective
tissue:-Binds,
supports and protects body parts, stores energy and minerals.
iii) Muscle
tissue:-Contracts
to produce movement.
iv) Nervous
tissue:-Initiates
and transmits nerve impulses that coordinate body activities.
Figure 1.7: Types of tissue
Ø Types
of star cluster
The group or cluster
of stars has known types such as,
i) Open
cluster:-It
contains from a dozen to many hundreds of stars, usually in an unsymmetrical
arrangement.
ii) Globular
cluster:-It
contains from thousands to hundreds of thousands of stars closely packed in a
symmetrical, roughly spherical form. The open cluster and globular cluster similarly
as epithelial tissues and connective tissues. From this point of view, more
group of stars we don’t know yet..! According to this, other discoveries and
studies of star clusters will be essayer than now.
!!! Cells are
stars and tissues are group of stars in human body universe...!!!
Figure 1.8: Open and Globular cluster
Ø Organs
It is collection
of millions of tissues which group together to perform single function in our
body universe. There are almost 78 organs in human body universe which vary
according to their size, function or action. Out of 78 organs Skin is larger
organ with respect to size and weight. The major organ in the body of human is
the brain, which is primarily responsible for performing all the functions and
actions of the body. With the preview of earlier sections, the Organs are galaxies
and group of organs are the group of galaxies. The organs and group of organs
are galaxies and group of galaxies in our human body universe.
Ø Formation
of Galaxies
Till yet we really
don’t know how various galaxies are formed and how
they took many
shape that we see today. But we do have some ideas about their origins and
evolution.
Shortly after
blast of big bang about 14 billion years ago, collapsing gas
and dust clouds
might have led to the formation of galaxies.
Interactions
between galaxies, specifically collisions between galaxies play an important
role in their evolution.
By the Hubble’s
law lead to the idea that, the universe is expanding.
We can estimate
the age of the universe based on the rate of expansion.
Because some
galaxies are billions of light years away from us, we can
discern that
they formed fairly soon after the big bang (as you look deeper and deeper into
the space, you will see further back in time). Most galaxies formed early but
data from NASA’s Galaxy Explorer (GALEX) telescope indicate that some new
galaxies have formed relatively recent within the past few billion years.
Most of theories
about the early universe make two assumptions..
1. It was filled
with hydrogen and helium.
2. Some areas
were slightly denser than others.
From these
assumptions, astronomers believe that the denser areas
slowed the
expansion slightly, allowing gas to accumulate in small protogalactic cloud. In
this cloud, gravity caused the gas and dust to collapse and form stars. These
stars burnt out quickly and become globular clusters but gravity continued to
collapse the clouds. As the clouds collapsed they form rotating disk. The
rotating disk attracted more gas and dust and formed galactic disk. Inside the
galactic disk new stars formed.
What remains on
the outskirts of the original cloud were globular clusters and the halo
composed of gas, dust and dark matter.
First solve the
question that we know exactly how the galaxies were
formed in the
universe.....???
Still answer is
mysterious.....Right !!
If we observe
how the organs were formed in our body universe then
maybe we will
reach at unique solution that of how the galaxies were
formed..!!
Ø Brain
of Human and Cosmos
The human brain
is one of the largest and most complex organ in the human body universe. It is
made up of more than 100 billion nerves that
communicate in
trillions of connections we call them as synapses. The
function of
Synapses is to transfer electrical or chemical signal (information) from one
cell to another. The transfer can be from nerve to nerve (nuero-neuro) or nerve
to muscle (neuro-myo).
The universe
also has its brain but yet we don’t know what it is..??
Also it is communicating
with all heavenly bodies, only thing is that we
Figure 1.9: Very small part of Synapses
We know 5000
synapses in the width of a hair...!!
Ø Mysteries
of Universe
Now we need to think
about it....
How galaxies
were formed...??
What is the
brain of universe...??
How they
communicating i.e.which frequency they are using...??
How and who is
expanding this universe...??
If we
comparatively study our human body universe and big bang universe, may be some
unknown mysteries will be solve much earlier than present..........
Reference and Links
http://scienceblogs.com/startswithabang/files/2010/04/history.
bigbang.jpeg
https://www.google.co.in/cell_evolution_tree_diagram.jpg
http://www.buzzle.com/images/diagrams/cell-division/meiosis1.
jpg
http://www.buzzle.com/images/diagrams/cell-division/meiosis2.
jpg
http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/biocoach/images/
cells/allcell.jpg
http://images.nationalgeographic.com/wpf/media-live/photos/
000/423/overrides/space166-globular-star-clusters_42308_
600x450.jpg
http://scienceblogs.com/startswithabang/files/2011/03/heic0603c.
jpeg
http://www.freethought-forum.com/images/anatomy4/interphase.
gif
http://fc08.deviantart.net/fs70/f/2011/332/b/1/mitosis_diagram_
by_l1ke20n1njas-d4hmraq.png
http://www.speed-light.info/images/star_nova.jpg
http://ridge.icu.ac.jp/gen-ed/cell-lect-gifs/09nucleus-diag.
GIF
http://s1197.photobucket.com/user/kevintanzm/media/tissue.
jpg.html
http://blog.sciencekicksass.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/10/
iStock_000025371965XSmall.jpg
Writer:
http://scienceblogs.com/startswithabang/files/2010/04/history.
bigbang.jpeg
https://www.google.co.in/cell_evolution_tree_diagram.jpg
http://www.buzzle.com/images/diagrams/cell-division/meiosis1.
jpg
http://www.buzzle.com/images/diagrams/cell-division/meiosis2.
jpg
http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/biocoach/images/
cells/allcell.jpg
http://images.nationalgeographic.com/wpf/media-live/photos/
000/423/overrides/space166-globular-star-clusters_42308_
600x450.jpg
http://scienceblogs.com/startswithabang/files/2011/03/heic0603c.
jpeg
http://www.freethought-forum.com/images/anatomy4/interphase.
gif
http://fc08.deviantart.net/fs70/f/2011/332/b/1/mitosis_diagram_
by_l1ke20n1njas-d4hmraq.png
http://www.speed-light.info/images/star_nova.jpg
http://ridge.icu.ac.jp/gen-ed/cell-lect-gifs/09nucleus-diag.
GIF
http://s1197.photobucket.com/user/kevintanzm/media/tissue.
jpg.html
http://blog.sciencekicksass.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/10/
iStock_000025371965XSmall.jpg
Writer: